What is the base station in HVAC?
The core principle of base station with pump and boiler control technology is to establish a wired network that connects the pump and boiler equipment to a base station. The base station interacts with the devices through sensors and actuators, and communicates with a central control system via a wired connection. The central control system can monitor and control the pumps and boilers in real time based on predefined parameters and algorithms. This wired connection ensures stable communication, reduces the possibility of wireless signal interference, and improves system reliability and response speed.
There are two types of base station. One is a wired where all products are connected via wires, and the other is a wireless base station where the thermostat is connected wirelessly and the others are controlled via wired connections. The thermostat transmits signals to the base station and then controls the thermal actuator.
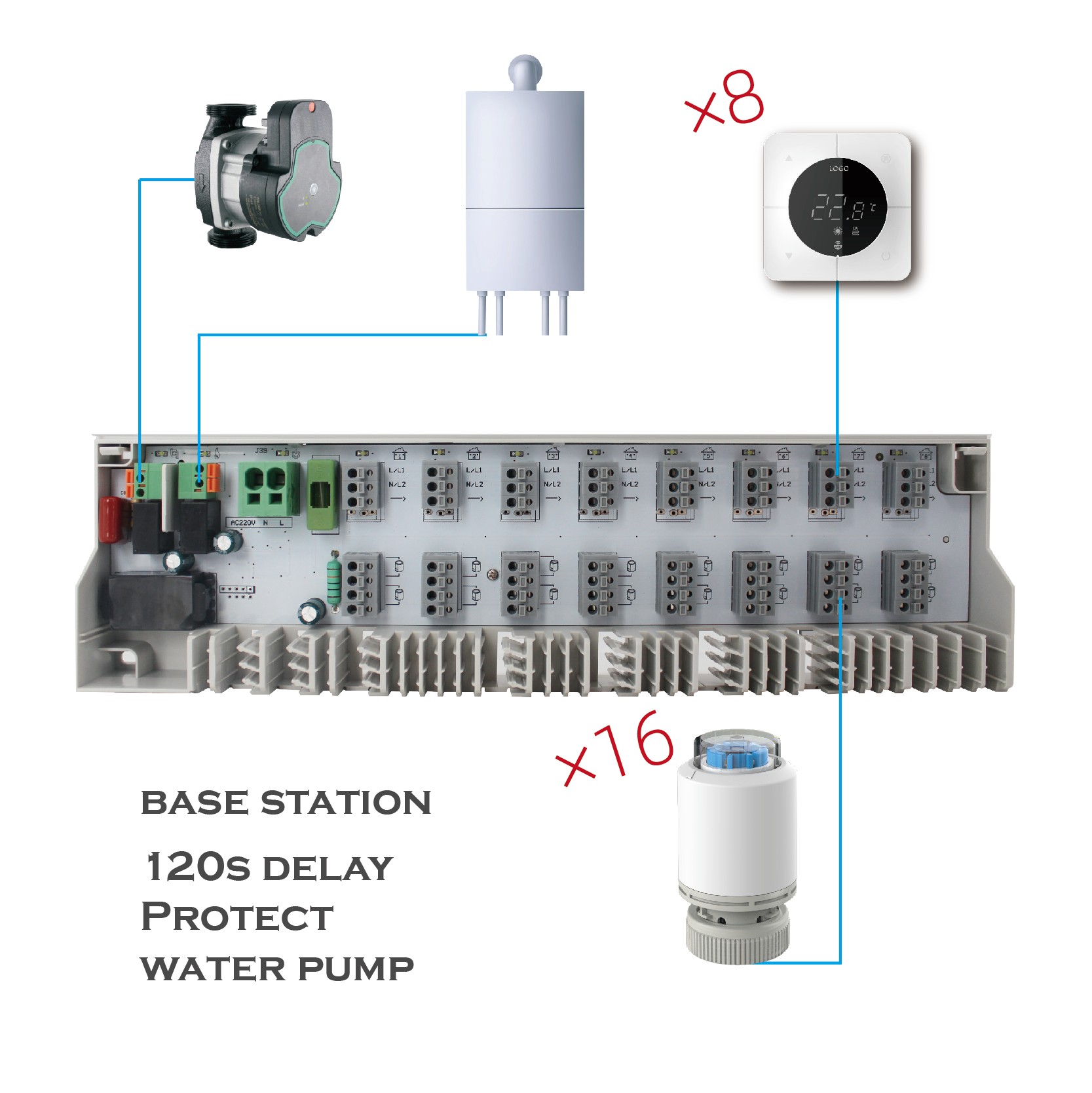

In the realm of HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) systems, a base station refers to a centralized control unit or module that effectively manages and monitors various components of the HVAC system. Here are the key aspects of a base station:
1.Centralized Control: The base station acts as the central hub from which all HVAC equipment and subsystems are monitored and controlled. It interfaces with thermostats, sensors, dampers, actuators, and other devices within the HVAC network.
2.Monitoring and Management: It continuously monitors critical parameters such as temperature, humidity levels, air flow rates, and overall system status. This real-time data allows for swift adjustments and optimizations of HVAC operations to maintain optimal comfort conditions efficiently.
3.Communication Hub: Typically, the base station communicates with remote sensors and control units distributed throughout the building or facility. It employs various communication protocols, both wired and wireless, to gather data and send commands to HVAC equipment.
4.Energy Efficiency: By centrally managing HVAC operations based on real-time data and predefined settings, the base station plays a pivotal role in optimizing energy consumption. This capability translates into substantial energy savings and enhanced operational efficiency.
5.Integration with Building Automation Systems (BAS): Modern base stations are often seamlessly integrated into broader building automation systems. This integration facilitates coordinated control of HVAC, lighting, security, and other building systems, thereby enhancing overall system performance.
6.User Interface: Base stations typically feature intuitive user interfaces such as touchscreen displays or web-based dashboards. These interfaces enable facility managers or building occupants to monitor system performance, adjust settings, and troubleshoot issues efficiently.
7.Customizable User Experience: Depending on the manufacturer and model, base stations may offer customizable user interfaces. This includes personalized dashboards, graphical representations of system performance, and prioritized displays of critical information, enhancing ease of management.
8.Fault Detection and Diagnostics (FDD): Many base stations integrate advanced algorithms for fault detection and diagnostics. These algorithms analyze data from sensors and equipment to detect potential issues or inefficiencies in the HVAC system proactively. Early identification of such issues helps prevent larger problems or system breakdowns.
In summary, a base station in HVAC systems serves a crucial function in centralizing control, optimizing energy efficiency, and ensuring comfort conditions within buildings or facilities. It represents a fundamental component in modern building management strategies aimed at improving operational effectiveness and sustainability.