What’s inside an HVAC system?
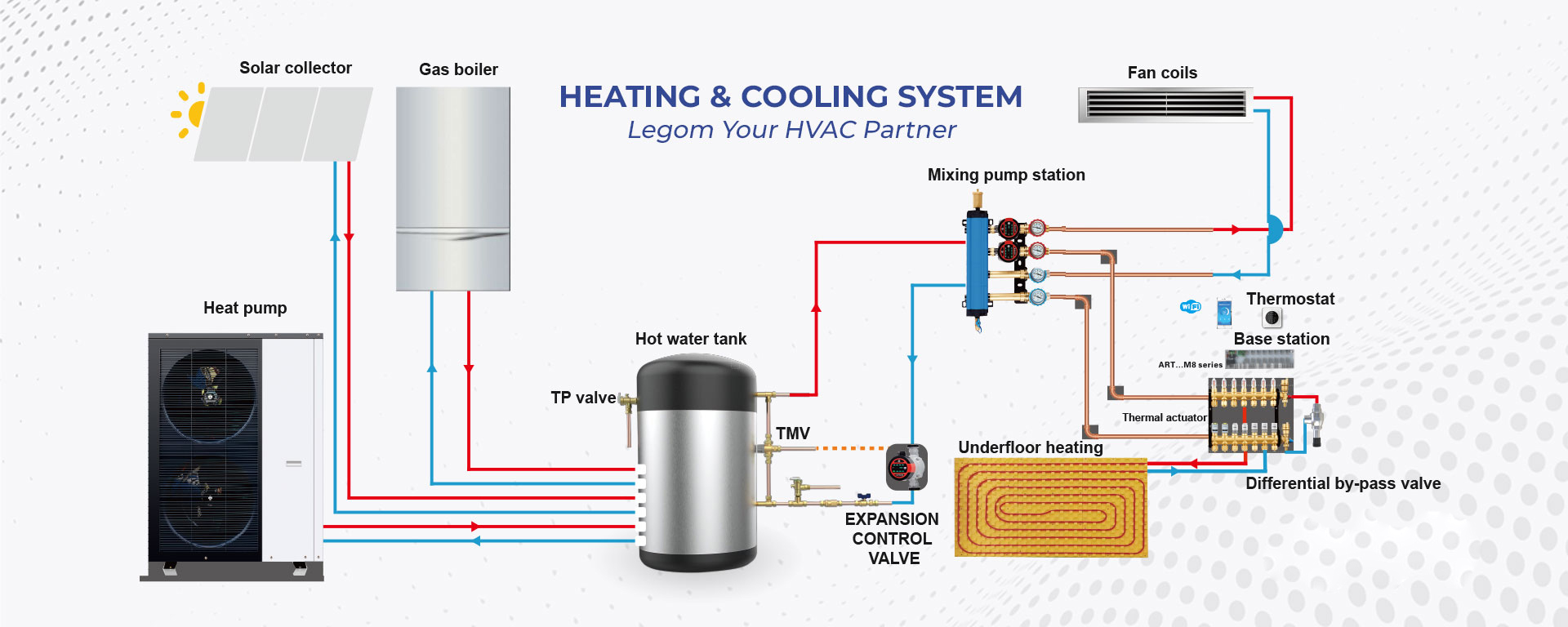
In the realm of modern building infrastructure, the heartbeat of comfort and efficiency pulsates through the intricate network of HVAC systems. From the initial conceptualization to the meticulous engineering and eventual installation, each component plays a pivotal role in orchestrating the symphony of climate control. In this article, we delve into the intricacies of one such HVAC system, dissecting its constituent parts, unraveling its inner workings, and illuminating its profound impact on the built environment.
Boiler: It is a device that uses the heat energy released by fuel combustion or other thermal energy to heat water or other working fluids.(Click here to learn more)
Solar panels or electricity: provide power to all equipment in the entire HVAC system and maintain its operation.
Water tank: has the function of storing water and exchanging water. As a part of the HVAC system, the buffer water tank plays a role in decompressing and protecting the running host. If the buffer water tank is not installed, the unit may start frequently. "When the control flow is low, the unit is more likely to trigger an alarm.". Insufficient water flow will cause many problems. Therefore, during the operation of the secondary power supply system, the matching of the buffer water tank is very important and is a standard accessory.(Click here to learn more)
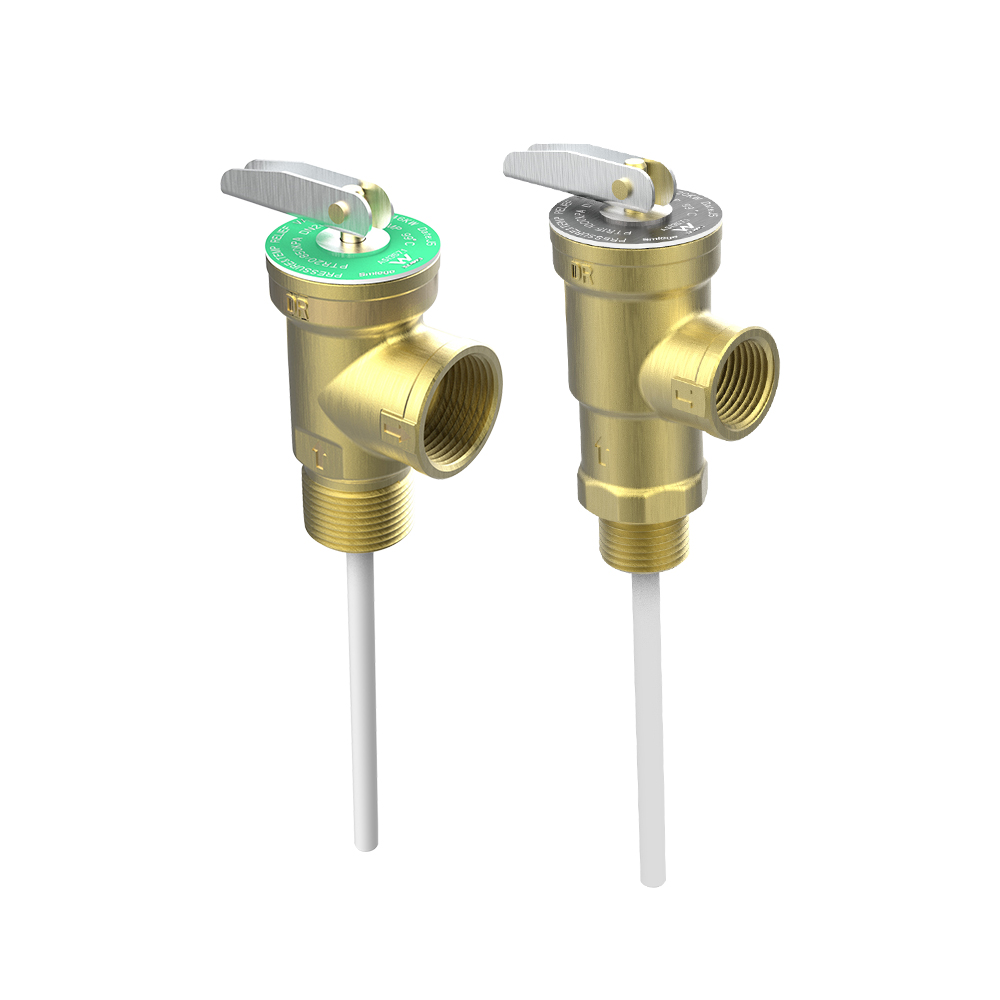

TP valve: The TP valve, also called temperature and pressure safety valve, is a pressure relief valve that integrates overpressure protection and overtemperature protection. It is suitable for pressure-bearing solar water heaters, electric water heaters, gas water heaters, and other equipment. Its main function is to effectively prevent the failure of the temperature control system of pressure-bearing hot water devices or the explosion of the water storage tank caused by the increase in temperature and pressure caused by scale blockage.(Click here to learn more)
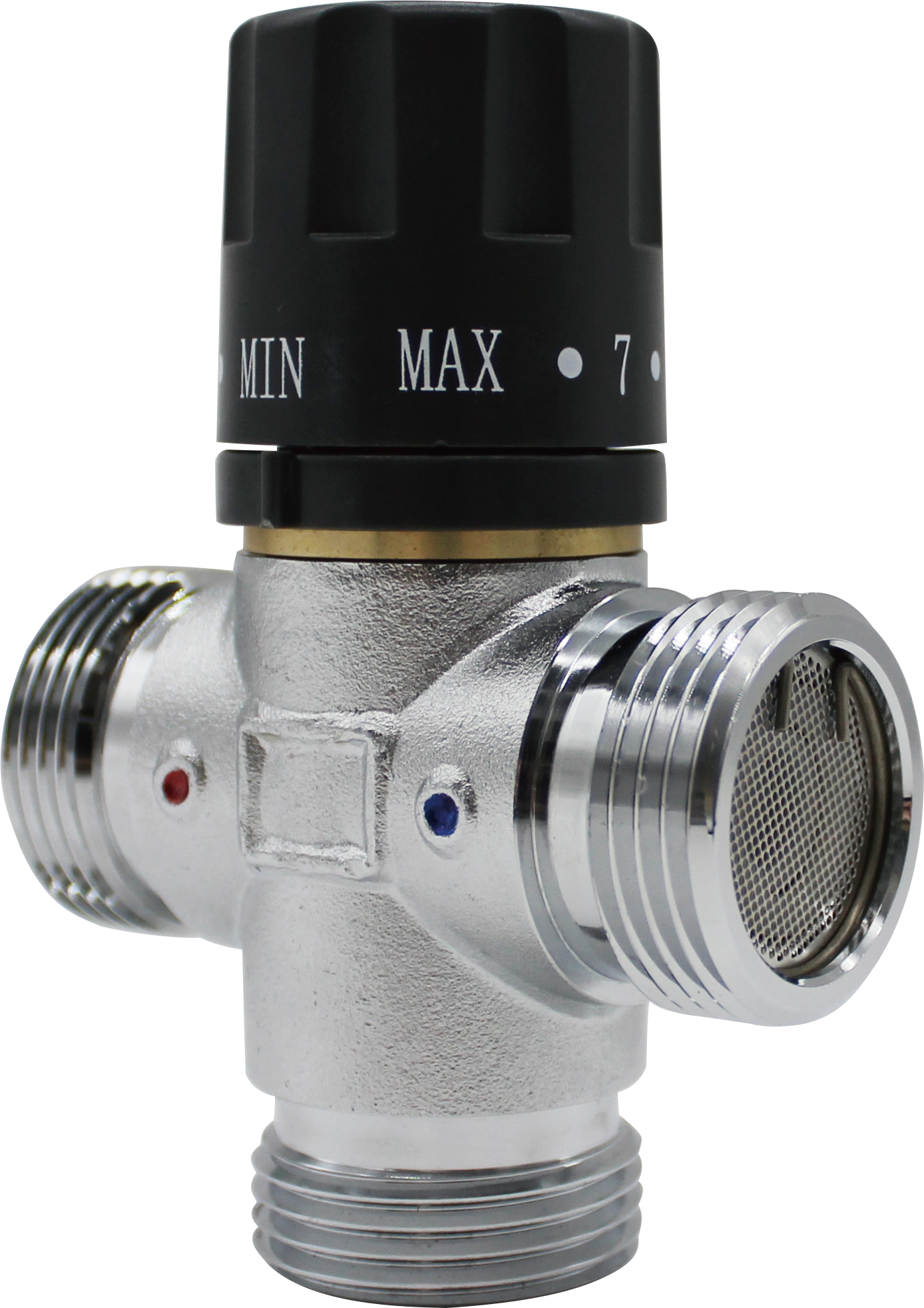

Mixing valve: A mixing valve is a valve that mixes hot and cold water. The valve itself cannot be mixed. It is only connected to the cold and hot water pipes and plays a mixing role. It is divided into manual mechanical adjustment type and self-operated thermostatic type. The former product is more popular.(Click here to learn more)
Mixing water system: The mixed water heat exchange regulation system is also called the heat exchange control center. It consists of an electric four-way regulating valve or a three-way regulating valve, a circulating water pump, a ball valve with a temperature meter, a proportional and integral controller, and a temperature sensor, It is composed of a filter valve, an electric regulating valve, water collector device, and heat exchange center.
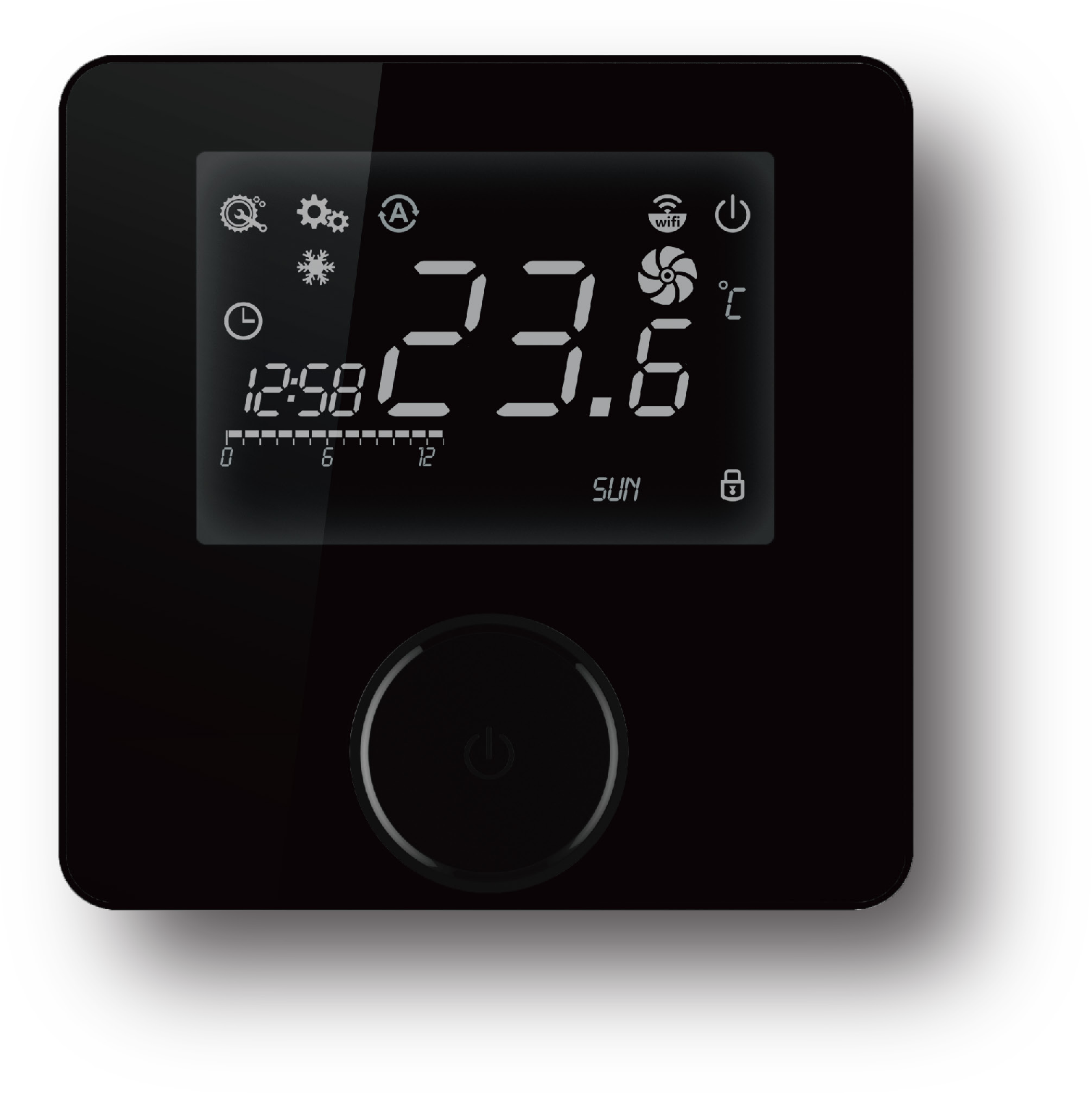
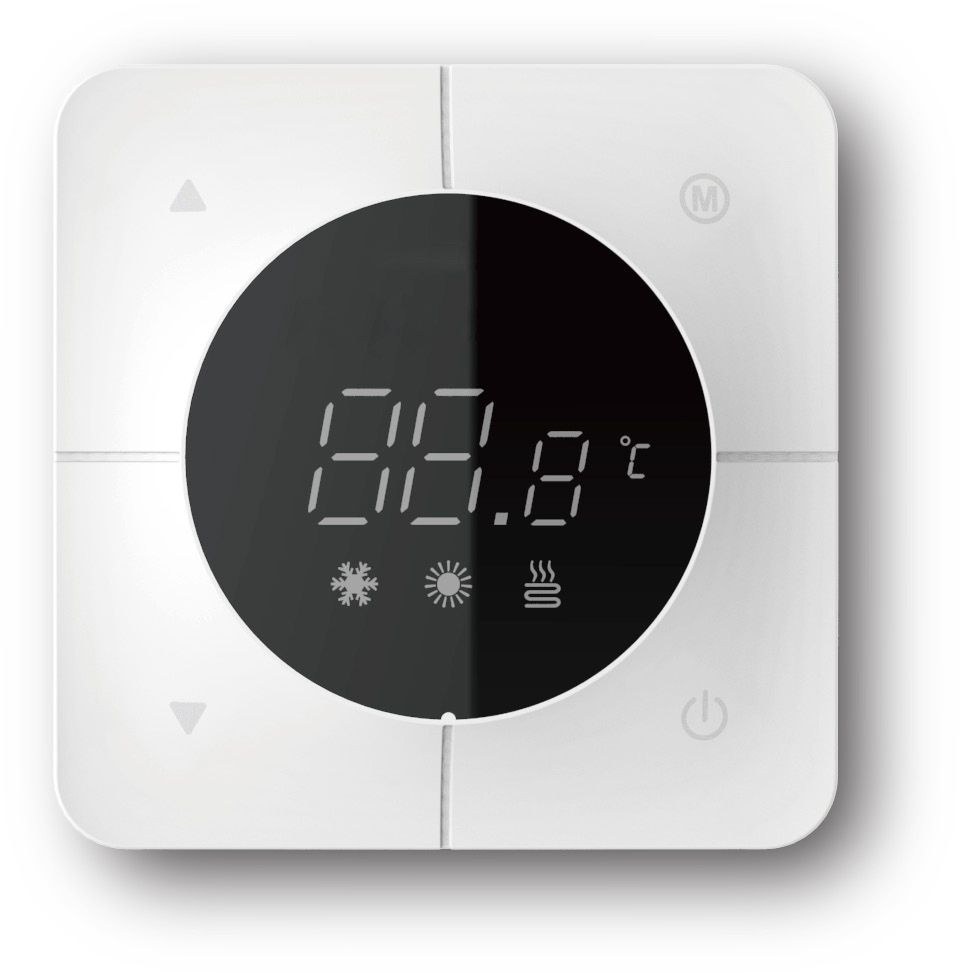
Room thermostat: A device used to control the temperature in a floor heating system to start its shutdown and other operations. Some advanced models can be remotely controlled by mobile phones and controlled and programmed to set the time and temperature you need.
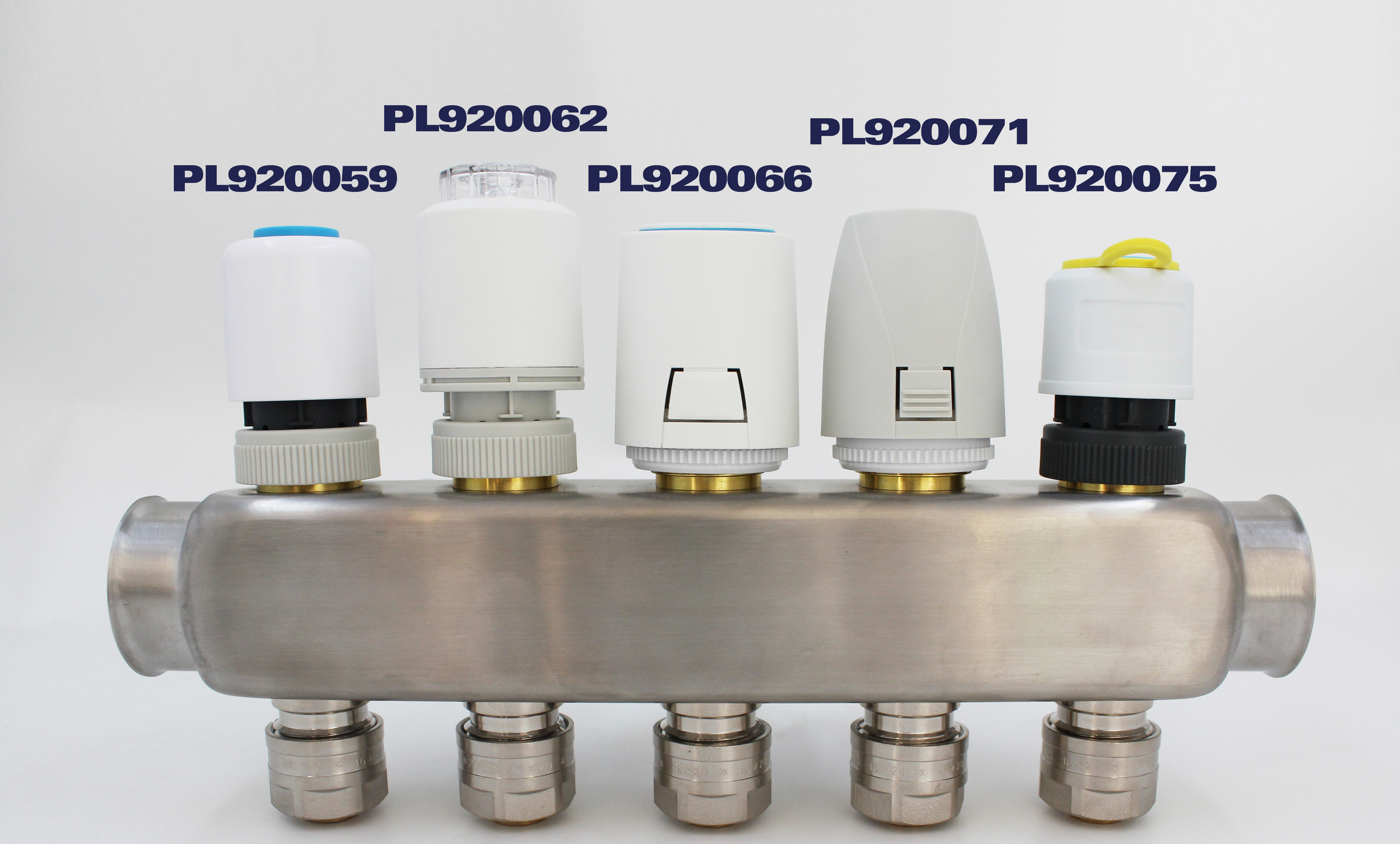

Thermal actuator: Installed on the water collector, it is used to receive signals from the thermostat to control the inflow and outflow of water.
Base station: a signal transfer station used to connect other equipment, as well as a power transmission center.

Manifold: Installed on the wall, it guides the water flow from the mixed water center to all corners of the room through its lines.
Self-acting Differential Pressure Bypass Valve: The differential pressure bypass valve is a valve used to balance the pressure difference between the supply/return water of the air conditioning system. This valve can improve the utilization of the system, maintain the precise mutual value of the pressure difference, and minimize the noise of the system and the damage to the equipment caused by excessive pressure difference. The opening can also be adjusted according to the terminal heat load. Even when the terminal load is very small or zero, a certain amount of water can be ensured to pass through the air conditioning unit, which protects the air conditioning unit and also plays a role in energy saving and consumption reduction.

Floor heating pipe: Floor heating pipe refers to a type of pipe used as a circulating flow carrier of low-temperature hot water in a low-temperature hot water floor radiant heating system (referred to as floor heating).
Fan coil: In the air conditioning system, the fan coil refers to the fan coil, which is the terminal device of the air conditioning system. Its working principle is that the unit continuously recirculates the air in the room where it is located and cools (heats) the air through the cold water (hot water) coil to maintain a constant room temperature.
As we draw the curtains on our exploration of this HVAC system, we are reminded of the profound fusion of science and engineering that underpins its functionality. From the humble beginnings of air intake to the final exhale of conditioned air, every element harmonizes to create an environment conducive to productivity, comfort, and well-being. As we look to the future, the evolution of HVAC technology promises even greater efficiency, sustainability, and resilience in the face of ever-changing environmental challenges. Truly, the legacy of innovation in HVAC engineering continues to shape the landscape of modern living, ensuring that the pursuit of comfort remains as timeless as it is indispensable.
Please follow us, and we will introduce each component of the system step by step.